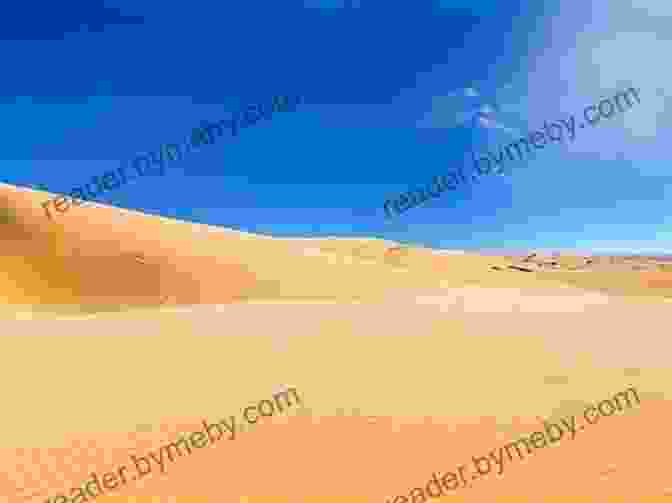
Desert Biomes Around the World: Exploring Earth's Arid Wonders

4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 19028 KB |
| Print length | : | 32 pages |

to Desert Biomes
Desert biomes are captivating and enigmatic ecosystems that defy the limits of life on Earth. Despite their harsh and unforgiving conditions, they harbor a remarkable diversity of life that has adapted to thrive in this arid environment. Deserts encompass a wide range of habitats, from the parched sands of the Sahara to the icy wastes of the Antarctic.
Essential Characteristics of Deserts
Deserts are defined by their extreme dryness, receiving less than 250 millimeters of precipitation per year. This scarcity of water shapes the entire ecosystem, leading to low levels of plant cover and a unique suite of adaptations among its inhabitants.
Water scarcity is not the only defining characteristic of deserts. They are also characterized by high temperatures, with many experiencing extreme diurnal fluctuations. Sand dunes, formed by wind erosion, are a common feature in many deserts, creating a dynamic and ever-changing landscape.
Types of Desert Biomes
The diversity of desert biomes around the world is astounding, each with its own unique characteristics. The three main types of deserts are hot and dry, semi-arid, and cold deserts.
Hot and Dry Deserts
Hot and dry deserts, such as the Sahara and Atacama, are the most extreme type of desert biome. They receive very little rainfall, with temperatures often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius during the day. The vegetation is sparse, consisting mainly of scattered shrubs and cacti.
Semi-Arid Deserts
Semi-arid deserts receive slightly more precipitation than hot and dry deserts, but are still very dry environments. They are characterized by the presence of grasslands and shrublands, as well as some trees.
Cold Deserts
Cold deserts, such as the Gobi and Patagonian deserts, are located in high-latitude regions or at high altitudes. They experience extreme temperatures, with freezing nights and warm days. Vegetation is limited to hardy grasses and shrubs.
Adaptations to Desert Life
Life in the desert presents significant challenges, but the diverse organisms that call these environments home have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive and thrive.
Plant Adaptations
Desert plants have developed a range of adaptations to conserve water. Some, like cacti, store water in their thick stems. Others, like succulents, have fleshy leaves that store water and reduce water loss through transpiration.
Animal Adaptations
Desert animals have also evolved unique adaptations to cope with the harsh conditions. Many are able to conserve water by excreting minimal amounts of urine and feces. Some animals, like camels, can store water in their humps. Others, like lizards, are able to absorb water through their skin.
Ecological Significance of Deserts
Despite their arid conditions, deserts play a crucial role in the global ecosystem. They serve as reservoirs of carbon dioxide and dust, influencing the global climate. Desert soils are also rich in minerals, which are essential for plant growth.
Threats to Desert Biomes
Desert biomes are facing a range of threats, including climate change, land conversion, and pollution. Increased temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns are leading to desertification, the expansion of desert-like conditions into non-desert areas.
Conservation and Education
Preserving desert biomes is essential for maintaining global biodiversity and ecosystem services. Conservation efforts should focus on reducing human impacts, protecting critical habitats, and promoting sustainable land management practices.
Education plays a vital role in raising awareness about the importance of deserts and fostering a sense of stewardship for these unique ecosystems. Through outreach programs, research, and protected areas, we can ensure that future generations can continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of desert biomes.
Desert biomes are a testament to the resilience of life on Earth. Despite their harsh conditions, they support
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 19028 KB |
| Print length | : | 32 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia William Silvester
William Silvester Walt Browning
Walt Browning Peter Bowerman
Peter Bowerman Mark Huber
Mark Huber Martin Mosebach
Martin Mosebach Shafiullah S A
Shafiullah S A Laura Lee
Laura Lee Rachael Bell Irving
Rachael Bell Irving Maurice R Greenberg
Maurice R Greenberg Steven Arms
Steven Arms Simon Clark
Simon Clark Moritz Fink
Moritz Fink Staci Swider
Staci Swider Tom Babin
Tom Babin Mark Wandrey
Mark Wandrey Marc Sedaka
Marc Sedaka Robert Collins
Robert Collins Marla Frazee
Marla Frazee Marian Lindberg
Marian Lindberg Michael Chandler
Michael Chandler
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Octavio PazEmbark on an Unforgettable Ski Adventure in the Aiguilles Rouges Mont Blanc:...
Octavio PazEmbark on an Unforgettable Ski Adventure in the Aiguilles Rouges Mont Blanc:...
 Derrick HughesHow I Became a Professional Hockey Fan: Dive into the Electrifying World of...
Derrick HughesHow I Became a Professional Hockey Fan: Dive into the Electrifying World of... Jayson PowellFollow ·3.2k
Jayson PowellFollow ·3.2k Neil ParkerFollow ·18.3k
Neil ParkerFollow ·18.3k Harry HayesFollow ·2.4k
Harry HayesFollow ·2.4k Jarrett BlairFollow ·3.5k
Jarrett BlairFollow ·3.5k Bill GrantFollow ·14.8k
Bill GrantFollow ·14.8k Andy HayesFollow ·12.5k
Andy HayesFollow ·12.5k Darren NelsonFollow ·5.9k
Darren NelsonFollow ·5.9k Tony CarterFollow ·17.1k
Tony CarterFollow ·17.1k

 Wayne Carter
Wayne CarterThe Beginner's Guide to Making an Old Motor Run Forever
If you're like most...

 Deacon Bell
Deacon BellNepali Adventure: Kings and Elephant Drivers,...
In the heart of the...

 Carlos Drummond
Carlos DrummondThe Romantic Revolution: A Journey Through History and...
Unveiling the...

 Kazuo Ishiguro
Kazuo IshiguroUnlock Your Inner Innovator: Dive into the New Wave...
Embark on a Transformative Journey of...

 William Golding
William GoldingCrazy Horse: The Lakota Warrior's Life and Legacy
In the annals of Native...

 Hector Blair
Hector BlairMildred and Richard Loving: The Inspiring Story of...
Mildred and Richard Loving were an...
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 19028 KB |
| Print length | : | 32 pages |